You might have detected a great opportunity based on a fair amount of traffic to your site from a specific country. Perhaps a PR campaign went viral, and now users worldwide look for your product, creating a constant demand for it.
Whatever the reason, an expansion, a new product launch or a diversification will always have to be supported by a prompt, detailed analysis of every element not only in the wider strategy but in SEO, too.
Entering a new market or going global comes with potentially significant rewards and considerable risks.
Search marketers usually agree on what factors contribute to market entrants’ success, including:
- Extensive keyword and competitor research.
- Target market persona analysis.
- Analysis of new entrants.
- Self-contained ecosystems to allow paid and digital PR campaign planning.
These studies will determine whether the brand can enter a new market, if the timing is right, or if there’s an opportunity to scale. Essentially, these are the main factors of success in any market entry or global launch.
In this article, you will discover six elements that worked for me when entering new markets while working for previous clients.
Before we dive in, it is important to note that every brand, agency and market is different. There is no single checklist that should be applied to your work.
Adapt this and other advice to your strategy and ensure it is aligned with wider business goals. Most importantly, finalizing a strategy involves working closely with other departments in your organization.
1. Market profitability assessment
International keyword research
In-depth analysis and keyword research in your target market is crucial to your international expansion strategy, as they will:
- Enable you to gather information on the search volume and traffic from words and phrases related to your product or service in the original languages of new markets.
- Show you potential variations in the language used (remember that translation and localization are not enough now).
Aside from search traffic, keyword difficulty is an important indicator since it specifies how competitive your keywords can be in various languages, regions and language fusions.
This article on international keyword research and intent is a great start.
Important tip: If you plan to translate your current set of keywords, make sure they are not only translated and localized but also they are aligned to how people search in your target country.
For example, in the north of Mexico and some parts of the Southern U.S., “Spanglish” is common. This means that in this part of the world, you will find many queries are done by mixing English and Spanish.
Take the fashion term “maxi dress” as an example. In Spain, people would search for “vestido largo,” whereas in some parts of Mexico, people might search for “maxi vestido.”
The example below is from Zara Mexico, where the way people search has influenced how products and categories are presented. As mentioned, the products are called “vestido maxi.”

Whereas in Zara Spain, similar products are called “vestido largo.”

In-depth international keyword research will:
- Give you an idea of the resources and capabilities you must have to enter the new market.
- Help you decide whether you are ready to expand or if it is better to wait.
Google Analytics data
Analyze your top converting traffic sources using Google Analytics (or other tracking software). Pay attention to the areas around the world where your brand is getting constant traffic.
While traffic is important, make sure to analyze conversions and revenue before deciding to expand to a new market.
Conduct an in-depth report, as this will help determine whether you can satisfy the demand emerging from these new countries.
Will you need a new warehouse? If you can’t have a new warehouse, you may need a communication strategy to emphasize delivery times.
Along with this, you might consider an incentive campaign to increase conversions if your delivery times might affect them.
Get the daily newsletter search marketers rely on.
2. Social networks in the target market
This is one of the most important steps when entering a new market.
You might be thinking that this is not related to SEO. It might not be at first glance.
However, it will determine the strategy for paid media and the type of content you should produce to increase brand awareness and gain links.
Why are social networks important?
Because a large percentage of online consumers start their purchase journey with brand research on social networks.

However, is important to note that:
- Not all consumers will always start their brand research on social networks.
- If they start on social networks, it is not always TikTok.
The chart below shows several age brackets and where they typically start their brand research, especially when making a high-value purchase.
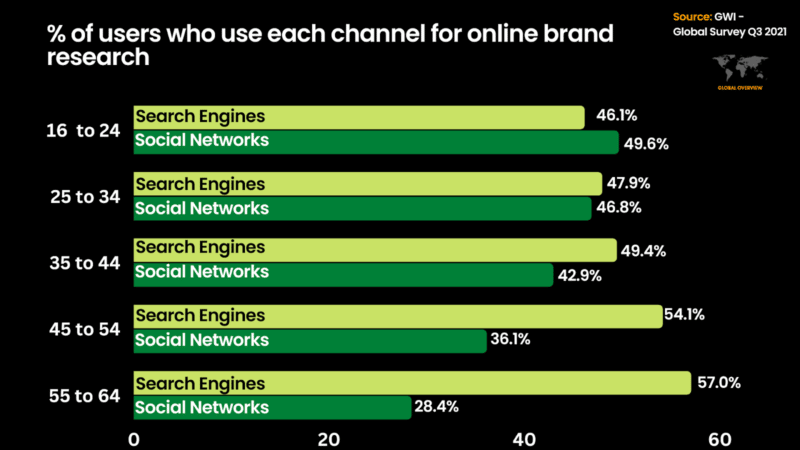
This information is useful when planning:
- The types of content to create for digital PR.
- The types of influencers to work with.
- The correct paid media channels for launching in a new market.
In some instances, the paid campaign will be on social networks, and in others, it will be more effective via Google Ads.
It is crucial to identify the main social networks used in the target country you are looking to expand in, especially for the age brackets that start their brand research on social. In some countries, it could be TikTok, while in others, it could be Instagram.
3. Hreflang
The hreflang is a little snippet of code that looks like this: rel="alternate" hreflang="X".
An hreflang tag should be added if your site has the same content in various languages.
In a global context, the hreflang element assists search engines in determining which URL version of your site should be provided to visitors from a given region or who speak a specific language.
Hreflang contributes toward a good user experience as it:
- Helps deliver a search result in the location and language the user made the query.
- Prevents duplicate content issues.
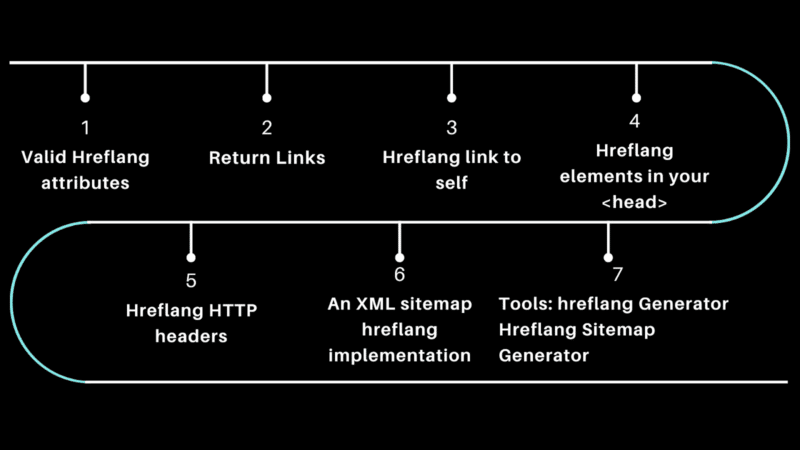
Below, I have included some ideas to consider when implementing hreflang.
- Valid hreflang attributes.
- Return links.
- Hreflang link to self.
- Hreflang elements in your
<head>. - Hreflang HTTP headers.
- An XML sitemap hreflang implementation.
- Tools: hreflang generator, hreflang sitemap generator.
4. URL structure
Similar to the hreflang principle of serving your users with results relevant to their language and location, the choice of the URL structure is crucial as it will be an indication for both search engines and users.
Here are the differences and uses of common URL structures: ccTLD, gTLD, subdomain and parameter.

There’s no “one size fits all” when it comes to URL structure. The choice should depend on your objectives and goals.
However, you should consider the limitations of your CMS. This is one reason why you might see some brands still using parameters. While using them is acceptable, parameters are not the best option.
Translating and localizing content is not enough. More than that, content should be aligned with common uses and language phenomena in your target country (i.e., Spanglish).
This principle also applies to your website’s shopping cart. When a customer is about to finish a purchase, it’s vital to consider the following:
- Currency: The currency must be the same as the user’s country.
- Language: It must be the same as your user’s country.
- Payment methods: Make sure you include Apple Pay (crucial), Google Pay, various credit cards and payment methods such as Klarna and Paypal.
- Information on delivery and choices for faster and cost-effective delivery methods.
- Discount code section.
If your target customers are between the ages of 16 to 34, consider that they are 80% more likely to pay with Apple Pay than with other methods.
Not having the preferred payment method, incorrect language, and unclear information will lead to cart abandonment.
6. International digital PR
Establishing a country-specific link strategy for each market is a must. Depending on your brand’s niche, you might be limited to a few tactics.
If you are in the food, fashion, sports or gifts sectors, the best course of action will be to identify the most used social network by your target audience and work with influencers in those appropriate channels.
Working with a relevant influencer in an appropriate social network and running paid campaigns are the best ways to enter a new market while you lay the groundwork for your organic efforts.
The beauty of digital PR is that there are plenty of opportunities to increase brand awareness and earn links.
If there isn’t a traditional PR team in your brand, you can focus on these tactics:
- Brand monitoring.
- Events.
- Content for promotion.
- Influencers.

To build valuable partnerships, it’s crucial always to adjust your approach to the customs of the individual market.
A sample approach can go like this:
- Identify influencers on TikTok.
- Establish collaborations.
- Create assets to promote on media outlets.
- Work with paid Media.
- Earn local links to add relevance and boost trust.
Read “Using digital PR to earn links and rank for your target keywords” to get started.
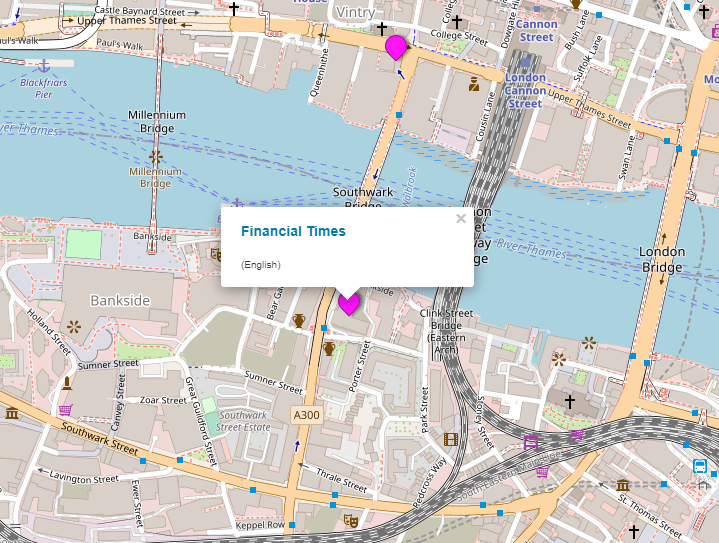
You can also refer to Newspaper Map, an interactive map that shows you online outlets available in every region you could imagine in the world.

When you click the pink bubbles, it will display a link to a specific online newspaper.
The following is an example when zooming into central London, where you’ll see the Financial Times’ office location.
Once you have identified your media outlet of choice and wish to connect to a journalist to request a link or a collaboration, you can use RocketReach (a tool where you can manually get the contact details of journalists).
Go global with the right SEO approach
The most common causes of failure when expanding include:
- Impulsivity. Making expensive decisions based on temporarily high product demand from a specific location.
- Common biases.
- Insufficient analysis.
- Poor strategy.
Your SEO team can have the best strategy. However, not working with other teams and having poor negotiation skills may lead to friction, poor implementation, and failure within the first two years of the expansion.
To avoid costly mistakes, it is important to do an in-depth study per element mentioned in this article – plus more.
Don’t base your expansion strategy on a checklist. Adapt resources to the knowledge of your business and the organization’s overall plan.
The following table shows the common biases in a market entry and ideas on how to tackle them.
| Core market entry analysis | Description | Common biases | How to tackle |
| Value Proposition | Business model. Do I have the necessary resources? | Impulsivity and egocentric interpretation of resources. | Determine the degree of variations in required capabilities for the new market. |
| Market size | Geographic area to expand, and how much demand is there? | Overconfidence, Anchoring and inadequate initial value. | Make decisions based on forecasts made on competitors in the target market. |
| Competition | Existing competitors in the market Potential entrants | Competitive blindspots | In-depth analysis of possible competitors and related sectors to our target market. |
| Estimates of market share revenue | Expectations of sales for our offering | Failing to consider the competitive response of existing competitors | Conduct in-depth competitor research. |
| Detailed cost estimates | Costs of input, distribution and economies to be faced | Underestimation of costs | Once all your cost plans are complete, it is advisable to hire an external consultant or auditor to review them to determine feasibility and potential risks. |
Remember that the success factors in an expansion are:
- Timing.
- Ability to leverage assets.
- Scalability.
- And, more than anything, work as a team!
Opinions expressed in this article are those of the guest author and not necessarily Search Engine Land. Staff authors are listed here.
New on Search Engine Land





